How To Filter Report Access 2013
Lesson 9: Sorting and Filtering Records
/en/access2013/working-with-forms/content/
Introduction
Admission gives you lot the power to piece of work with enormous amounts of data, which ways it can be difficult to larn anything nigh your database just by glancing at it. Sorting and filtering are 2 tools that let you customize how yous organize and view your data, making information technology more user-friendly to piece of work with. In this lesson, you'll learn how to sort and filter records
Throughout this tutorial, we will be using a sample database. If you would like to follow along, you'll need to download our Admission 2013 sample database. You will need to have Access 2013 installed on your computer in club to open the example.
Well-nigh sorting and filtering
Essentially, sorting and filtering are tools that let you organize your data. When you lot sort data, you lot are putting it in order. Filtering data lets yous hibernate unimportant information and focus simply on the data you're interested in.
Sorting records
When y'all sort records, you are putting them into a logical order, with similar data grouped together. Every bit a outcome, sorted data is often simpler to read and empathise than unsorted data. By default, Access sorts records by their ID numbers. Withal, in that location are many other ways records can be sorted. For example, the information in a database belonging to a bakery could exist sorted in a number of ways:
- Orders could exist sorted by gild date or by the last name of the customers who placed the orders.
- Customers could be sorted by proper name or past the city or zilch lawmaking where they live.
- Products could be sorted by proper name, category (like pies, cakes, and cupcakes), or price.
Yous tin sort both text and numbers in ii means: in ascending social club and descending order. Ascending ways going up, so an ascending sort volition arrange numbers from smallest to largest and text from A to Z. Descending means going downwardly, or largest to smallest for numbers and Z to A for text. The default ID number sort that appears in your tables is an ascending sort, which is why the lowest ID numbers appear get-go.
In our example, we will be performing a sort on a tabular array. Nonetheless, you tin can sort records in whatsoever Access object. The procedure is largely the same.
To sort records:
- Select a field you lot want to sort by. In this example, we volition sort by customers' last names.
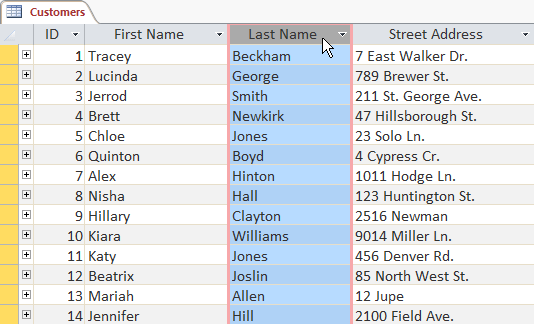 Selecting a field by clicking on its title
Selecting a field by clicking on its title - Click the Home tab on the Ribbon, and locate the Sort & Filter group.
- Sort the field by selecting the Ascending or Descending command.
- Select Ascending to sort text A to Z or to sort numbers from smallest to largest. We will select this in our case considering we want the last names to be in A-to-Z order.
- Select Descending to sort text Z to A or to sort numbers from largest to smallest.
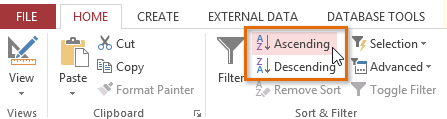 The Ascending and Descending Sort commands
The Ascending and Descending Sort commands - The tabular array volition at present be sorted by the selected field.
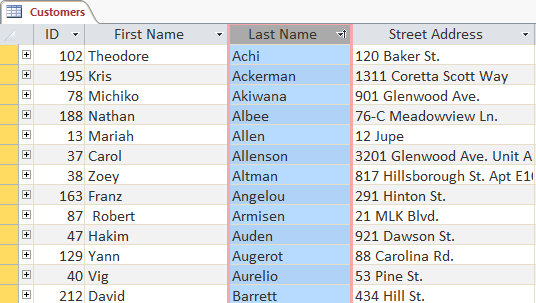 The same table with an ascending sort applied to the Terminal Name field
The same table with an ascending sort applied to the Terminal Name field - To save the new sort, click the Relieve control on the Quick Access toolbar.
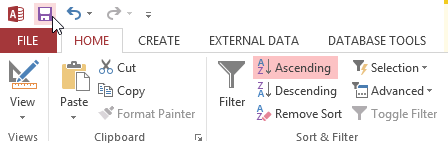 Saving the sort
Saving the sort
After you lot salve the sort, the records will stay sorted this mode until you perform another sort or remove the current one. To remove a sort, click the Remove Sort command.
 Removing the sort
Removing the sort
Filtering records
F ilters allow you lot to view only the data yous want to run into. When you create a filter, y'all prepare criteria for the information y'all want to brandish. The filter so searches all of the records in the table, finds the ones that meet your search criteria, and temporarily hides the ones that don't.
Filters are useful because they let you to focus in on specific records without existence distracted by the data you lot're uninterested in. For instance, if you had a database that included client and order data, you could create a filter to display merely customers living within a certain urban center or simply orders containing a sure product. Viewing this data with a filter would exist far more than user-friendly than searching for it in a big table.
In our examples and explanations, we volition be applying filters to tables. However, you can apply filters to whatever Admission object. The procedure is largely the same.
To create a simple filter:
- Click the drop-downwards arrow next to the field y'all want to filter by. Nosotros will filter by metropolis because nosotros desire to see a list of customers who live in a certain city.
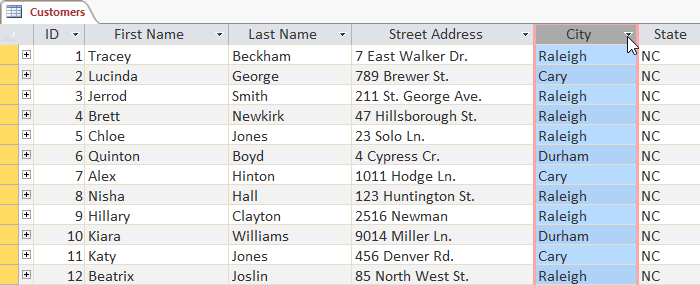 Selecting a field to sort by
Selecting a field to sort by - A driblet-down carte du jour with a checklist will appear. Only checked items will be included in the filtered results. Use the following options to determine which items will exist included in your filter:
- Select and deselect items i at a time past clicking their checkboxes.
- Click Select All to include every item in the filter. If all items are already selected, this selection will deselect all items.
- Click Blanks to set the filter to discover only the records with no data in the selected field.
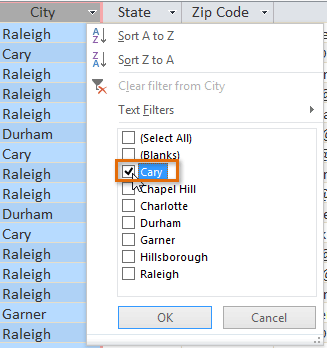 Setting the filter to only bear witness records with "Cary" in the metropolis field
Setting the filter to only bear witness records with "Cary" in the metropolis field - Click OK. The filter will be applied. Our customers table now displays only customers who live in Cary.
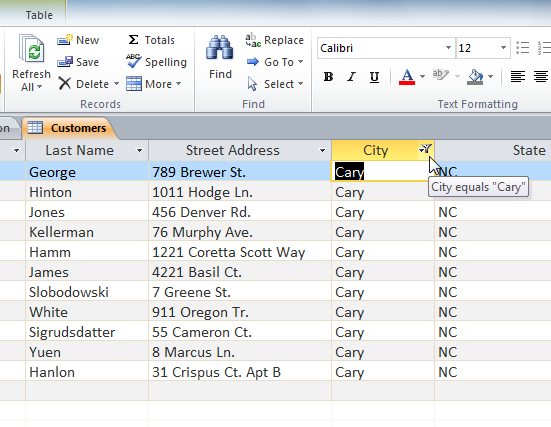 The filtered table, at present showing only the records for customers who live in Cary
The filtered table, at present showing only the records for customers who live in Cary
Toggling your filter allows you to turn information technology on and off. To view the records without the filter, click the Toggle Filter control. To restore the filter, click it again.
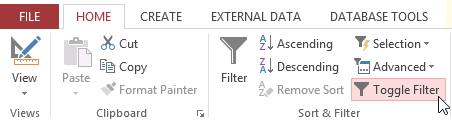 Removing the current filter with the Toggle Filter command
Removing the current filter with the Toggle Filter command
Creating a filter from a selection
Filtering by selection allows yous to select specific data from your tabular array and detect data that is similar or dissimilar to it. For example, if you lot were working with a baker'southward database and wanted to search for all products whose names independent the word chocolate, you could select that word in one product name and create a filter with that choice. Creating a filter with a option tin be more user-friendly than setting upwardly a simple filter if the field you're working with contains many items.
To create a filter from a selection:
- Select the cell or information you want to create a filter with. We want to see a list of all of our products that contain the word chocolate in their names, then nosotros'll select the word chocolate in the Production Proper noun field.
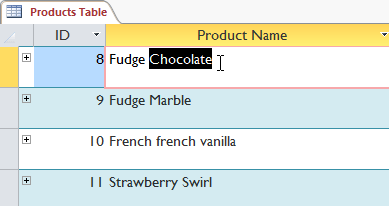 Selecting text to filter for
Selecting text to filter for - Select the Domicile tab on the Ribbon, locate the Sort & Filter group, and click the Selection driblet-down arrow.
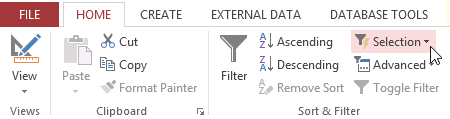 Clicking the Filter by Choice command
Clicking the Filter by Choice command - Select the type of filter yous want to apply:
- Contains includes only records with cells that contain the selected data. We'll select this considering we desire to see records that contain the word chocolate anywhere in the title.
- Does Non Contain includes all records except for those with cells that contain the selected data.
- Ends With includes only records whose information for the selected field ends with the search term.
- Does Non Cease With includes all records except for those whose information for the selected field ends with the search term.
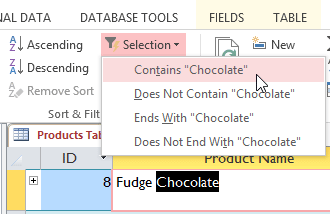 Setting the filter to prove simply records that contain the selected discussion
Setting the filter to prove simply records that contain the selected discussion
- The filter will be practical. Our table now displays merely products with the discussion chocolate in their names.
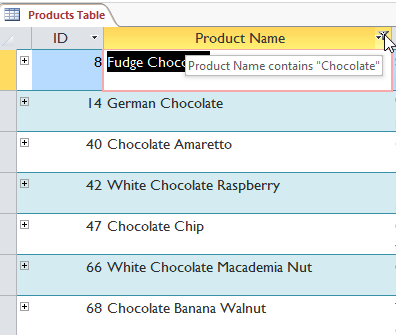 The filtered table showing only records containing "chocolate" in the Product Proper name field
The filtered table showing only records containing "chocolate" in the Product Proper name field
Creating a filter from a search term
You tin too create a filter past entering a search term and specifying the mode Access should match data to that term. Creating a filter from a search term is like to creating a filter from a pick.
Filtering text by a search term
When filtering text by entering a search term, y'all can utilise some of the same options you apply when filtering by a pick, similar Contains, Does Not Contain, Ends With, and Does Not End With. You can besides cull from the following options:
- Equals, which includes only records with data that is identical to the selected data
- Does Not Equal, which includes all records except for the data that is identical to the selection
- Begins With, which includes only records whose data for the selected field begins with the search term
- Does Not Begin With, which includes all records except for those whose data for the selected field begins with the search term
To filter text past a search term:
- Click the drop-downwardly arrow side by side to the field yous want to filter by. We want to filter the records in our orders table to brandish only those that contain notes with certain information, so we'll click the arrow in the Notes field.
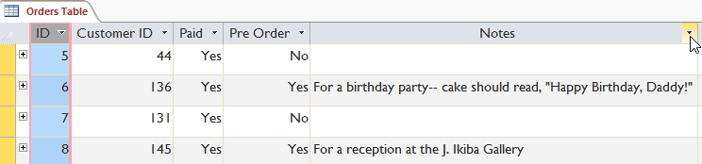 Selecting a field to filter past
Selecting a field to filter past - In the drop-downwardly bill of fare, hover your mouse over Text Filters. From the list that appears, select the mode you want the filter to match the term yous enter. In this example, we want to view only records whose notes indicate the order was placed for a party. We'll select Contains and so we tin can search for records that contain the word political party.
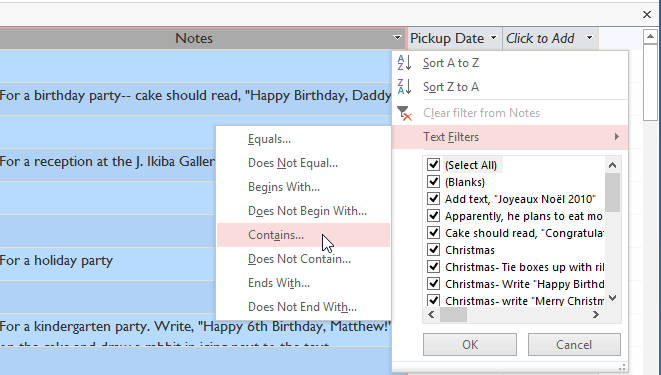 Selecting filter settings
Selecting filter settings - The Custom Filter dialog box will appear. Type the word you want to use in your filter.
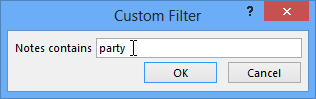 Typing the term the filter will search for
Typing the term the filter will search for - Click OK. The filter will exist applied.
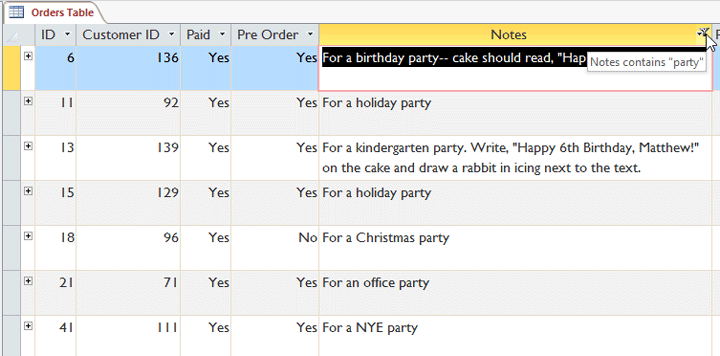 The filtered table showing simply records containing the give-and-take "party" in the Notes field
The filtered table showing simply records containing the give-and-take "party" in the Notes field
Filtering numbers with a search term
The process for filtering numbers with a search term is similar to the process for filtering text. All the same, different filtering options are bachelor to you when working with numbers. In addition to Equals and Does not Equal, you lot tin can choose:
- Greater Than to include only records with numbers in that field that are greater than or equal to the number you enter
- Less Than to include only records with numbers in that field that are less than or equal to the number yous enter
- Between to include records with numbers that fall within a certain range
To filter numbers by a search term:
- Click the drop-down arrow next to the field you want to filter by. We desire to filter the records in our menu items table by price, so we'll click the arrow in the Price field.
- In the drop-downwardly menu, hover your mouse over Number Filters. From the list that appears, select the way y'all want the filter to lucifer your search term. In this example, we desire to see items that are less than $5, so we'll select Less Than.
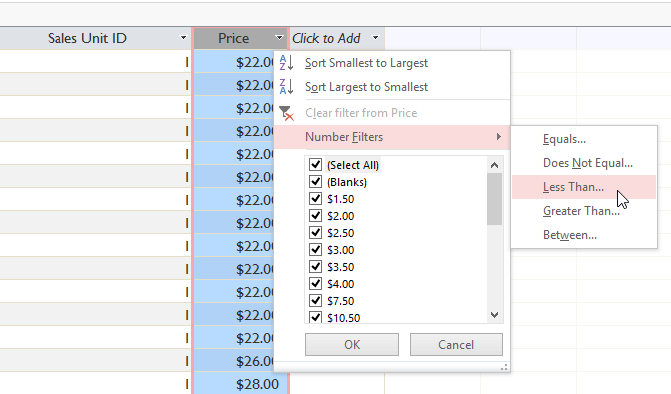 Selecting a field to filter by
Selecting a field to filter by - The Custom Filter dialog box will announced. Type the number or numbers you desire to apply in your filter. We'll type 5 then the filter volition show the states simply menu items that cost $5 or less.
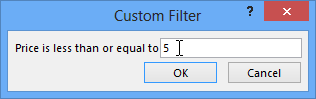 Typing the number to filter for
Typing the number to filter for - Click OK. The filter will be applied.
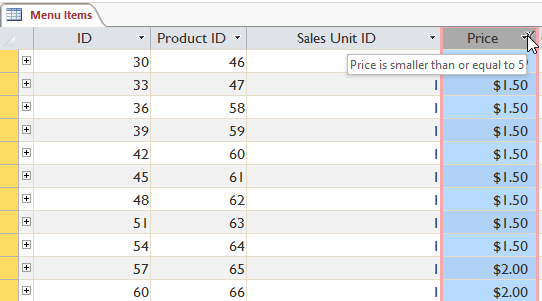 The filtered table showing only records for bill of fare items costing $v or less
The filtered table showing only records for bill of fare items costing $v or less
Specific types of numbers may include other filtering options. For example, dates stored in numerical form (mm/dd/yyyy, or 12/01/2013) include options to filter by periods of time.
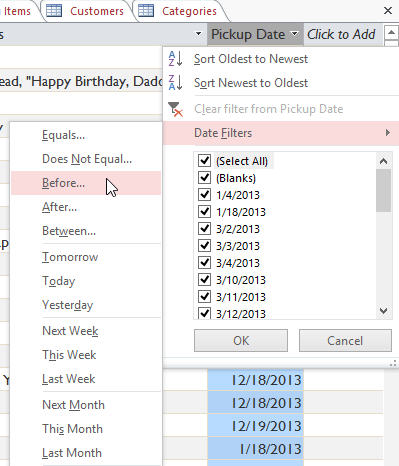 Filtering by date
Filtering by date
Challenge!
- Open up an existing Access database. If yous want, you tin can use our Admission 2013 sample database.
- Open the query called Cakes and Pies Sold.
- Apply a filter to the Product Types field that shows simply Cakes.
- In the Sum of Quantity field, apply a filter that only shows numbers greater than five.
- Apply an ascending sort to the Sum of Quantity field.
- Save the database.
/en/access2013/designing-a-simple-query/content/
How To Filter Report Access 2013,
Source: https://edu.gcfglobal.org/en/access2013/sorting-and-filtering-records/1/
Posted by: falconefifue1964.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Filter Report Access 2013"
Post a Comment